| Coronary
Angioplasty
Cardiac Catheterization Procedure (Coronary
Angiogram/ Angiography)
First, a cardiac catheterization
is performed. The patient receives medication for
relaxation. The doctor then numbs the area where the
procedure will be performed. A sheath (thin, plastic
tube) is inserted into an artery in the groin or sometimes
the arm. A long, slender tube called a catheter is
inserted through the sheath and guided through the
blood vessel to the arteries surrounding the heart.
A diagnostic procedure called coronary
angiography is performed next. During angiography,
a small amount of contrast material is injected through
the catheter and is photographed as it moves through
the heart's chambers, valves and major vessels. From
the digital photographs of the contrast material,
the doctors can tell whether the coronary arteries
are narrowed and/or whether the heart valves are working
correctly.
Interventional Procedures
An interventional procedure starts
out in the same way as a diagnostic cardiac catheterization.
Once the blocked artery is identified with the catheterization,
the doctor performs the interventional procedure.
There are several interventional procedures that may
be used to open the artery.
Balloon angioplasty
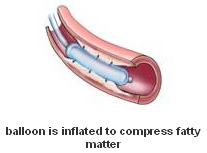 (Percutaneous
Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty or PTCA) A small
balloon at the tip of a specially designed catheter
is inflated to compress the fatty matter into the
artery wall and stretch the artery open to increase
blood flow to the heart. (Percutaneous
Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty or PTCA) A small
balloon at the tip of a specially designed catheter
is inflated to compress the fatty matter into the
artery wall and stretch the artery open to increase
blood flow to the heart.
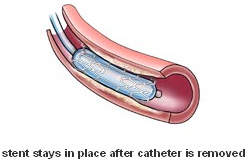
Stent
A stent is a small, metal mesh tube
that acts as a scaffold to provide support inside
the coronary artery. A balloon catheter, placed over
a guide wire, is used to insert the stent into the
narrowed coronary artery. Once in place, the balloon
is inflated and the stent expands to the size of the
artery and holds it open. The balloon is deflated
and removed, and the stent stays in place permanently.
Over a several-week period, the artery heals around
the stent. Stents are commonly placed during interventional
procedures such as angioplasty or atherectomy to help
keep the coronary artery open.
Drug-eluting stents (introduced
in 1993) contain medicine and are designed to reduce
the risk of reblockage (restenosis). Your interventionalist
will decide if a drug-eluting stent is appropriate
for your type of blockage.
|