| Hip Resurfacing
What is Hip Resurfacing?
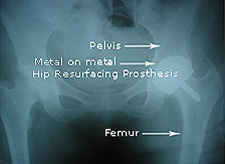 Hip
Resurfacing or Surface Replacement Arthroplasty is
a bone-conserving alternative to conventional Total
Hip Replacement (THR). Unlike Total Hip Replacement,
hip Resurfacing does not involve the removal of the
femoral head and neck nor removal of bone from the
femur. Rather, the head, neck and femur bone is preserved
in an effort to facilitate future surgery should it
be necessary and to enable the patient to take advantage
of newer technology or treatments in the future. Hip
Resurfacing or Surface Replacement Arthroplasty is
a bone-conserving alternative to conventional Total
Hip Replacement (THR). Unlike Total Hip Replacement,
hip Resurfacing does not involve the removal of the
femoral head and neck nor removal of bone from the
femur. Rather, the head, neck and femur bone is preserved
in an effort to facilitate future surgery should it
be necessary and to enable the patient to take advantage
of newer technology or treatments in the future.
The current generation of hip Resurfacing
devices utilize a metal bearings have demonstrated
a much higher level of wear resistance as well as
reduced bone loss and inflammatory tissue reaction
about the hip joint as compared to metal-polyethylene
bearings.
Hip Resurfacing is anatomically
and biomechanically more similar to the natural hip
joint resulting in increased stability, flexibility
and range of motion. Further, dislocation risk is
virtually eliminated. Higher activity levels are typically
achieved with less risk. These benefits are realized
because the head diameter that results from Resurfacing
is very similar to the patient's normal head diameter
and these larger head sizes are typically much larger
than the femoral balls utilized in conventional THR.
Advantages of Hip Resurfacing :
1. Allows the patient to squat and
sit on the floor safely
2. Allows a normal range of movement and sporting
activities after operation
3. Sacrifices only the diseased bone and preserves
normal bone
4. Restores the normal structures of the hip
5. More natural feel after surgery
6. Early rehabilitation
7. Easy to revise if needed
8. Less risk of dislocation
9. No leg length alteration
Know the physiology of Human Hip
The normal hip joint consists of
a ball rotating inside a socket. The ball is called
the head of the femur and the socket in the pelvis
is called the Acetabulum. The surface of the femoral
head and the acetabulum (i.e. the ball and the socket)
is covered by a protective layer of cartilage. This
makes the joint smooth and reduces friction during
movements. It covers and protects the bone like the
rubber of a car tyre.
Any condition that damages the Cartilage
will lead to pain, dysfunction and eventually arthritis.
Cartilage can get damaged due to a number of reasons
including Injury, Infection, Ankylosing Spondylitis,
Avascular Necrosis ( loss of blood supply to bone),
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis, Developmental
problem like bone Dysplasias, slipped upper femoral
epiphyses etc.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hip
Resurfacing
- Is this a minimally invasive?
This operation can be done by a
minimally invasive approach and the invasion can be
kept to less than 10cms.The operation also involves
minimal damage to bone.
- Do I need blood transfusion during the
surgery?
We generally do not need blood transfusions
during the operation.
- Is it a very painful operation?
Pain control techniques and minimal
injury to soft tissue and bone during surgery help
to keep the patients comfortable in the post operative
period.
- When do we remove the stitches and is
it very painful?
Absorbable sutures are used. These
need not to be removed. The patient does not have
to follow up for up to 60 years after discharge from
hospital.
- How long do I have to stay in hospital?
Local patients are discharged four
days after the operation, but overseas patients may
have to stay for 8-10 days after surgery.
- When can I start walking and climbing
stairs after the operation?
Most patients start walking with
support on the second postoperative day after removal
of the drain. Our team of physiotherapist takes you
through a standardized protocol of mobilization and
stair climbing is achieved before discharge.
- Do I need lots of physiotherapy after
surgery?
The amount of physiotherapy needed
depends on the condition of your joint and muscles
before the operation. Most patients do not need much
suppressed physiotherapy.
- Will I be able to sit on the floor after
surgery?
Yes, this surgery will allow you
to do that safely unless another problem prevents
it.
Hip resurfacing or surface replacement
arthroplasty uses specialized implants that are fixed
into the bone .Two international companies sell such
implants in India at present.
a)Smith and Nephew (MMT) - (BHR)
Birmingham Hip Resurfacing.
b)Johnson and Johnson - (ASR) Articular Surface Replacement.
- What is the advantage of Hip Resurfacing
over conventional total hip replacement?
Conventional Total Hip Replacements
usually consist of a long metal component that is
fixed into the femur (thigh bone) articulating with
a polyethylene cup cemented into the pelvis.
Conventional hip replacements sacrifice
a large quantity of normal bone. The very nature of
fixation of these implants causes progressive bone
loss due to stress shielding. The problem of bone
loss gets compounded by osteolysis due to polyethylene
debris from the cup. All these reduce the bone stock
and make any future revision procedures difficult.
The polyethylene cups gradually thin down due to wear
and need replacing. The head of the femoral component
is small in diameter, so as to reduce friction at
the cost of stability. This increases the risk of
hip dislocation i.e. hip coming out of joint.
Problems with Conventional Total Hip
Replacement:
1. Bone loss
2. Increased risk of dislocation
3. Cannot squat or sit on the floor
without the risk of dislocating the hip
4. Range of movement is less
5. Cannot safely indulge in sporting
activities
6. Revision Surgery difficult
7. Feels less like a normal natural
hip
8. Possibility of change in leg
length after surgery
Are there any implants used?
Modern techniques allow us to replace
the diseased human hip with artificial implants which
ensure near normal movements and function.
Huge advances have been made in
terms of the materials, the method of fixation and
structure of these implants. The purpose of all these
changes is to increase the longevity, reduce complication
rate and improved function after surgery. Hip Resurfacing
(bone conserving hip replacement (BHR), surface replacement
) with a metal-on-metal articulation is another step
in this direction.
|