| Cervical
Cancer
Basic Information
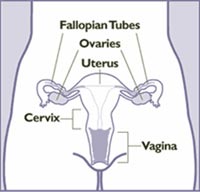 Cancer
is a disease in which abnormal cells in the body grow
out of control. When these abnormal cells are present
in the cervix, it is called cervical cancer, or cancer
of the cervix. As the drawing shows, the cervix is
the lower, narrower part of the uterus. The uterus
is also known as the womb. The upper part of the uterus
is where a baby grows when a woman is pregnant. The
cervix connects the upper part of the uterus to the
vagina (the birth canal). Cancer
is a disease in which abnormal cells in the body grow
out of control. When these abnormal cells are present
in the cervix, it is called cervical cancer, or cancer
of the cervix. As the drawing shows, the cervix is
the lower, narrower part of the uterus. The uterus
is also known as the womb. The upper part of the uterus
is where a baby grows when a woman is pregnant. The
cervix connects the upper part of the uterus to the
vagina (the birth canal).
A Pap test is a procedure in which
cells are scraped from the cervix and examined under
a microscope. It is used to detect cancer or changes
that may lead to cancer. A Pap test can also show
noncancerous conditions, such as infection or inflammation.
Getting regular Pap tests can save
a woman's life. Cervical cancer can usually be prevented
if precancerous cervical lesions are found by a Pap
test and treated. Invasive cervical cancer can usually
be cured if it is found early through regular Pap
tests and treated promptly. About half of the women
in the United States who develop cervical cancer have
never had a Pap test. Regular Pap tests decrease a
woman's risk for developing cervical cancer because
they can detect precancerous cervical lesions at early,
treatable stages.
Fast Facts
- Cervical cancer can usually be prevented if women
are screened regularly with a test called the Pap
test.
- Any woman who has a cervix can get cervical cancer,
especially if she or her sexual partner has had
sex with several other partners.
- Most often, cervical cancer develops in women
aged 40 or older.
- Abnormal cells in the cervix and cervical cancer
don't always cause symptoms, especially at first.
That's why getting tested for cervical cancer is
important, even if there are no symptoms.
- When it is found early and treated, cervical cancer
is highly curable.
- Most deaths from cervical cancer could be avoided
if women had regular checkups with the Pap test.
Risk Factors
Research has found several factors
that may affect a person's risk of developing cervical
cancer.
- Infection with certain types of human papillomavirus
(HPV).
- A high number of sexual partners.
- Many full-term pregnancies.
- Use of oral contraceptives.
- Infrequent Pap tests and cervical examinations.
- Smoking.
- Diet low in fruits and vegetables.
Screening Pap Test
What Is the Pap Test?
The Pap test, also called the Pap
smear, is a cervical cancer screening test. It is
not used to detect other kinds of cancer. It is done
in a doctor's office or a clinic. This test can find
abnormal cells in the cervix that may turn into cancer
if they're not treated.
During the test, the doctor or nurse
uses a plastic or metal instrument, called a speculum,
to widen the vagina. This helps the doctor or nurse
examine the vagina and the cervix, and collect a few
cells and mucus from the cervix and the area around
it. These cells are placed on a slide and sent to
a laboratory to be checked for abnormal cells.
The doctor or nurse also performs
a pelvic exam, checking the uterus, ovaries and other
organs to make sure there are no problems. There are
times when a doctor may perform a pelvic exam without
giving you a Pap test. Ask your doctor or nurse which
tests you're having, if you're unsure.
Who Should Have a Pap Test?
Doctors recommend that women begin
having regular Pap tests and pelvic exams at age 21,
or within three years of the first time they have
sexual intercourse-whichever happens first. National
guidelines recommend that after a woman has a Pap
test each year for three years in a row, and test
results show there are no problems, she can then get
the Pap test once every 2-3 years. For more information,
see Screening Recommendations. Who Does Not Need to
Be Tested?
The only women who do not need regular
Pap tests are Those over age 65 who have had several
regular Pap tests with normal results and have been
told by their doctors that they don't need to be tested
anymore.
Women who do not have a cervix.
This includes women whose cervix was removed as part
of an operation to remove the uterus. (The surgery
is called a hysterectomy.) However, a small number
of women who have had this operation still have a
cervix and should continue having regular Pap tests.
If you're not sure whether you have a cervix, speak
to your doctor about it.
How Do I Prepare for the Pap Test?
To prepare for the Pap test, doctors
recommend that for two days before the test you should
avoid
Douching
Using tampons
Having sexual intercourse
Using birth control foams, creams, or jellies, or
vaginal medications or creams
Doctors also recommend that you
try to schedule your Pap test for a time when you
are not having your menstrual period.
When Will I Get the Results?
It can take up to three weeks to
receive Pap test results. Most results are normal.
But if your test shows something may be abnormal,
the doctor or nurse will contact you and probably
want to do more tests. There are many reasons that
Pap test results can be abnormal, and usually it does
not mean you have cancer.
Amazon will work with you and our India
Affiliates to create a package where all your Cancer
concerns/problems can be addressed. If you have any
questions, please do not hesitate to contact us by
phone or email.
|