| Prostate
and Prostate Cancer
What is the prostate?
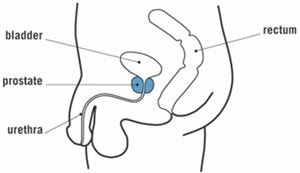 The
prostate is a walnut-sized gland that only men have.
It is part of the reproductive system that makes the
fluid that carries sperm. As you can see in the picture
below, the prostate is located in front of the rectum
and just below the bladder. The urethra (the tube
that carries urine from the bladder to outside the
body) runs through the center of the prostate. As
men age, the prostate tends to increase in size. This
can cause the urethra to narrow and decrease urine
flow. The
prostate is a walnut-sized gland that only men have.
It is part of the reproductive system that makes the
fluid that carries sperm. As you can see in the picture
below, the prostate is located in front of the rectum
and just below the bladder. The urethra (the tube
that carries urine from the bladder to outside the
body) runs through the center of the prostate. As
men age, the prostate tends to increase in size. This
can cause the urethra to narrow and decrease urine
flow.
What is prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer is made up of cells
that do not grow normally. The cells divide and create
new cells that the body does not need, forming a mass
of tissue called a tumor. These abnormal cells sometimes
spread to other parts of the body, multiply, and cause
death.
What causes prostate cancer?
As with many types of cancers, medical
experts do not know what causes prostate cancer. They
are studying several possible causes.
Can prostate cancer be prevented?
Medical experts do not know how
to prevent prostate cancer, but they are studying
many factors. They do know that not smoking, maintaining
a healthy diet, staying physically active, and seeing
your doctor regularly contribute to overall good health.
Who is at increased risk for prostate
cancer?
While all men are at risk for prostate
cancer, some factors increase risk:
Family history. Men with a father or brother who has
had prostate cancer are at greater risk for developing
it themselves.
Race. Prostate cancer is more common in some racial
and ethnic groups than in others, but medical experts
do not know why. Prostate cancer is more common in
African-American men than in white men. It is less
common in Hispanic, Asian, Pacific Islander, and Native
American men than in white men.
Is prostate cancer serious?
Some prostate cancers become a serious
threat to health by growing quickly, spreading beyond
the prostate gland to other parts of the body, and
causing death. Yet other prostate cancers grow slowly
and never become a serious threat to health or affect
how long a man lives. Doctors can't always be sure
what type of cancer is present in your particular
case.
What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?
Many men with prostate cancer often
have no symptoms. If symptoms appear, they can include
Blood in the urine
The need to urinate frequently, especially at night
Weak or interrupted urine flow
Pain or burning feeling while urinating
The inability to urinate
Constant pain in the lower back, pelvis, or upper
thighs
If you have any of these symptoms,
see your doctor as soon as possible. Keep in mind
that these symptoms are also caused by other prostate
problems that are not cancer, such as an infection
or an enlarged prostate.
Prostate Cancer Screening
What does "screening" mean?
Screening means looking for signs
of disease in people who have no symptoms. So screening
for prostate cancer is looking for early-stage disease
when treatment may be more effective. The main screening
tools for prostate cancer are the digital rectal examination
(DRE) and the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test.
The DRE and PSA test cannot tell if you have cancer;
they can only suggest the need for further tests.
What is the DRE?
The DRE or digital (finger) rectal
examination is a quick exam for checking the health
of the prostate. For this test, the doctor inserts
a gloved and lubricated finger into the rectum. This
allows the doctor to feel the back portion of the
prostate for size and any irregular or abnormally
firm areas.
What is the PSA test?
PSA stands for "prostate-specific
antigen." PSA is a substance produced by cells
from the prostate gland and released into the blood.
The PSA test measures the PSA level in the blood.
A small amount of blood is drawn from the arm. The
doctor checks the blood to see if the PSA level is
normal. The doctor may also use this test to check
for any increase in your PSA level compared to your
last PSA test.
Treating Prostate Cancer
What happens if prostate cancer is
found?
No two men with prostate
cancer are the same. Many factors affect the decision
whether or not to treat the disease: The
patient's age, whether the cancer has spread, the
presence of other medical conditions, and the patient's
overall health.
When prostate cancer has
been found in its early stages and has not spread
beyond the prostate, a doctor and his patient may
decide upon Watchful waiting: Monitoring
the patient's prostate cancer by performing the PSA
test and DRE regularly, and treating it only if and
when the prostate cancer causes symptoms or shows
signs of growing
Surgery (radical prostatectomy):
Removing the prostate
External radiation therapy:
Destroying cancer cells by directing radiation at
the prostate
Internal radiation therapy
(brachytherapy): Surgically placing small
radioactive pellets inside or near the cancer to destroy
cancer cells
Hormone therapy: Giving
certain hormones to keep prostate cancer cells from
growing
Cryotherapy: Placing
a special probe inside or near the prostate cancer
to freeze and destroy the cancer cells
More advanced prostate cancers that
have spread beyond the prostate can be complex to
treat and may be incurable. Patients should discuss
with their doctor the best course of action.
Do these treatments have side effects?
Side effects from prostate cancer
treatment depend mainly on the type of treatment,
the patient's age, and his overall health. Men can
experience pain, discomfort, and other mild to severe
side effects that may be temporary or may last a long
time. Two important side effects are impotence and
incontinence. When a doctor explains the treatment
options, he or she can discuss how mild or severe
side effects might be, and how long they might last.
Also, a doctor may be able to perform surgery or prescribe
drugs to relieve some side effects.
|