| Breast
Cancer
Basic Information
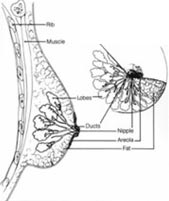 Cancer
is a disease in which abnormal cells in the body grow
out of control. Cancers are named after the part of
the body where the abnormal cell growth begins. Breast
cancers are cancer cells from the breast. When breast
cancer cells spread to other parts of the body, they
are called metastases. Cancer
is a disease in which abnormal cells in the body grow
out of control. Cancers are named after the part of
the body where the abnormal cell growth begins. Breast
cancers are cancer cells from the breast. When breast
cancer cells spread to other parts of the body, they
are called metastases.
Common Kinds of Breast Cancer
There are different kinds of breast
cancer. The kind of breast cancer depends on which
cells in the breast turn into cancer. Breast cancer
can begin in different parts of the breast, like the
ducts or the lobes.
Common kinds of breast cancer are
Ductal carcinoma
The most common kind of breast cancer. It begins in
the cells that line the milk ducts in the breast,
also called the lining of the breast ducts.
Ductal carcinoma
in situ (DCIS)
The abnormal cancer cells are only in the lining of
the milk ducts, and have not spread to other tissues
in the breast.
Invasive ductal
carcinoma
The abnormal cancer cells break through the ducts
and spread into other parts of the breast tissue.
Invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts
of the body.
Lobular carcinoma
In this kind of breast cancer, the cancer cells begin
in the lobes, or lobules, of the breast. Lobules are
the glands that make milk.
Lobular carcinoma
in situ (LCIS)
The cancer cells are found only in the breast lobules.
Lobular carcinoma in situ, or LCIS, does not spread
to other tissues very often.
Invasive lobular
carcinoma
Cancer cells spread from the lobules to the breast
tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells
can also spread to other parts of the body.
Fast Facts
Not counting some kinds of skin cancer,
breast cancer in the United States is
- The most common cancer in women, no matter your
race or ethnicity.
- The most common cause of death from cancer among
Hispanic women.
- The second most common cause of death from cancer
among white, black, Asian/Pacific Islander, and
American Indian/Alaska Native women.
In 2003 (the most recent year numbers
are available):
181,646 women and 1,826 men developed
breast cancer.
41,619 women and 379 men died from breast cancer.
Men can also get breast cancer.
In men, breast cancer can happen at any age, but is
most common in men who are between 60 and 70 years
old. Male breast cancer is not very common. For every
100 cases of breast cancer, less than 1 are in men.
For men, signs of breast cancer
and treatment are almost the same as for women.
Symptoms
Different people have different
warning signs for breast cancer. Some people do not
have any signs or symptoms at all. A person may find
out they have breast cancer after a routine mammogram.
Some warning signs of breast cancer
are
- New lump in the breast or underarm (armpit).
- Thickening or swelling of part of the breast.
- Irritation or dimpling of breast skin.
- Redness or flaky skin in the nipple area or the
breast.
- Pulling in of the nipple or pain in the nipple
area.
- Nipple discharge other than breast milk, including
blood.
- Any change in the size or the shape of the breast.
Pain in any area of the breast.
Keep in mind that some of these
warning signs can happen with other conditions that
are not cancer.
Screening
Kinds of Screening Tests
Breast cancer screening means checking
a woman's breasts for cancer before there are signs
or symptoms of the disease. Three main tests are used
to screen the breasts for cancer. Talk to your doctor
about which tests are right for you, and when you
should have them.
Mammogram
A mammogram is an X-ray of the breast. Mammograms
are the best method to detect breast cancer early
when it is easier to treat and before it is big enough
to feel or cause symptoms. Having regular mammograms
can lower the risk of dying from breast cancer. 1
If you are age 40 years or older, be sure to have
a screening mammogram every one to two years.
Clinical breast
exam
A clinical breast exam is an examination by a doctor
or nurse, who uses his or her hands to feel for lumps
or other changes. 2
Breast self-exam
A breast self-exam is when you check your own breasts
for lumps, changes in size or shape of the breast,
or any other changes in the breasts or underarm (armpit).
Diagnosis
Doctors often use additional tests
to find or diagnose breast cancer.
Breast ultrasound
A machine uses sound waves to make detailed pictures,
called sonograms, of areas inside the breast.
Diagnostic mammogram
If you have a problem in your breast, such as lumps,
or if an area of the breast looks abnormal on a screening
mammogram, doctors may have you get a diagnostic mammogram.
This is a more detailed X-ray of the breast.
Magnetic resonance
imaging (MRI)
A kind of body scan that uses a magnet linked to a
computer. The MRI scan will make detailed pictures
of areas inside the breast.
Biopsy
This is a test that removes tissue or fluid from the
breast to be looked at under a microscope and do more
testing. There are different kinds of biopsies (for
example, fine-needle aspiration, core biopsy, or open
biopsy).
Treatment
Kinds of Treatment
Breast cancer is treated in several
ways. It depends on the kind of breast cancer and
how far it has spread. Treatments include surgery,
chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, biologic therapy,
and radiation. People with breast cancer often get
more than one kind of treatment.
Surgery
An operation where doctors cut out and remove cancer
tissue.
Chemotherapy
Using special medicines, or drugs to shrink or kill
the cancer. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines
given through an intravenous (IV) tube, or, sometimes,
both.
Hormonal therapy
Some cancers need certain hormones to grow. Hormonal
treatment is used to block cancer cells from getting
the hormones they need to grow.
Biological therapy
This treatment works with your body's immune system
to help it fight cancer or to control side effects
from other cancer treatments. Side effects are how
your body reacts to drugs or other treatments. Biological
therapy is different from chemotherapy, which attacks
cancer cells directly.
Radiation
The use of high-energy rays (similar to X-rays) to
kill the cancer cells. The rays are aimed at the part
of the body where the cancer is located.
It is common for doctors from different specialties
to work together in treating breast cancer. Surgeons
are doctors that perform operations. Medical oncologists
are doctors that treat cancers with medicines. Radiation
oncologists are doctors that treat cancers with radiation.
|



 Cancer
is a disease in which abnormal cells in the body grow
out of control. Cancers are named after the part of
the body where the abnormal cell growth begins. Breast
cancers are cancer cells from the breast. When breast
cancer cells spread to other parts of the body, they
are called metastases.
Cancer
is a disease in which abnormal cells in the body grow
out of control. Cancers are named after the part of
the body where the abnormal cell growth begins. Breast
cancers are cancer cells from the breast. When breast
cancer cells spread to other parts of the body, they
are called metastases.