| Pain Management
 Description Description
Procedures to alleviate pain - e.g.
nerve blocks, intra-articular injections, etc
Machine
Using imaging guidance, such as
fluoroscopy, USG or CT, we can now guide therapy,
mainly in the area of relieving pain.
Preparation/Instructions
Pre-procedure workup
Procedure
There are many procedures that can
be performed, some of which include; suprascapular
blocks for frozen shoulders, lumbar Sympathectomies
for unremitting pain from peripheral vascular disease,
disco grams for evaluating discal pain, facet and
SI joint blocks and vertebroplasties, etc.
Basically any procedure that alleviates
pain, but needs necessary guidance with an imaging technique
can be performed.
Suprascapular Nerve Blocks
Frozen shoulder or peri-arthritis
is a condition that results in significant disability,
wherein the patients are unable to move their arms
at the shoulder and have pain and discomfort.
 It
is usually a self-limited procedure and takes approx.
9 months for recovery. Apart from anti-inflammatory
medication, graded physiotherapy and on occasion,
intra-articular steroid injections and arthroscopic
adhesiolysis are used to treat more difficult cases. It
is usually a self-limited procedure and takes approx.
9 months for recovery. Apart from anti-inflammatory
medication, graded physiotherapy and on occasion,
intra-articular steroid injections and arthroscopic
adhesiolysis are used to treat more difficult cases.
The suprascapular nerve in the suprascapular
notch has approximately 70% of the sensory supply
from the capsule. By blocking this nerve, it is possible
to reduce the pain significantly and allow movement
of the shoulder. This in turn, facilitates physiotherapy
and helps faster recovery.
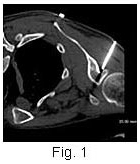
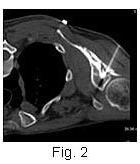 This
procedure is performed under CT guidance in the prone
position. Once the needle is in place, a steroid and
anesthetic mixture is injected (Figs. 1, 2). Usual
improvement is within 24 hours and can last from 3-6
months. Repeated injections are possible, but the
most important role seems to be the ability to allow
aggressive physiotherapy to be conducted. This
procedure is performed under CT guidance in the prone
position. Once the needle is in place, a steroid and
anesthetic mixture is injected (Figs. 1, 2). Usual
improvement is within 24 hours and can last from 3-6
months. Repeated injections are possible, but the
most important role seems to be the ability to allow
aggressive physiotherapy to be conducted.
 Lumbar
Sympathectomies Lumbar
Sympathectomies
These are most commonly performed
to alleviate pain in patients with severe peripheral
vascular disease. By ablating the lumbar sympathetic
plexus, the blood flow to the limbs is increased and
this helps in relieving pain.
The effect lasts for 1 week to 2
years, but the period is unpredictable from patient
to patient.
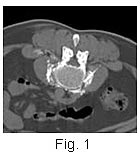
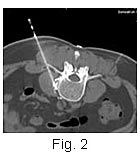 The procedure is performed under
CT guidance and two needles are simultaneously placed
on either side of the upper margin of the L3 vertebral
body (Figs. 1, 2). For temporary
relief, bupivicaine is injected, but for permanent
ablation, absolute alcohol is used. The procedure is performed under
CT guidance and two needles are simultaneously placed
on either side of the upper margin of the L3 vertebral
body (Figs. 1, 2). For temporary
relief, bupivicaine is injected, but for permanent
ablation, absolute alcohol is used.
|